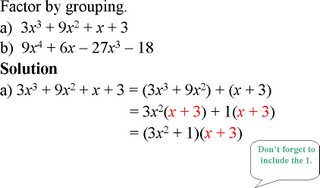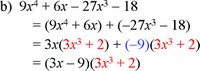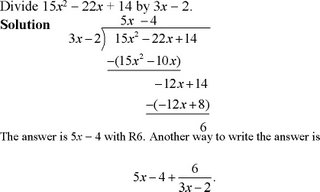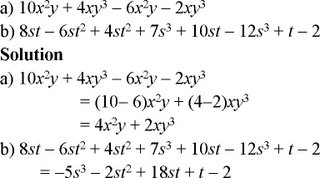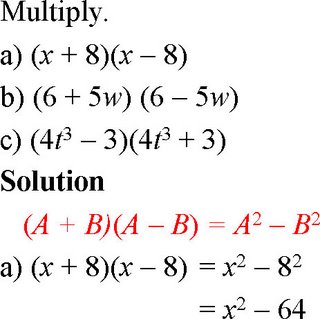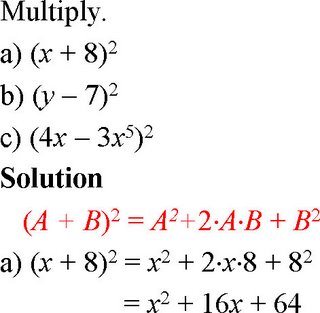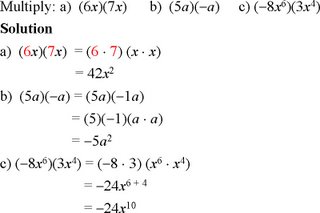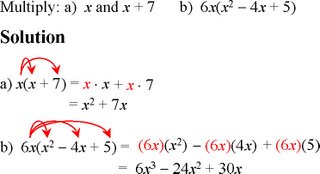Polynomials: Factoring 5.1
5.1 INTRODUCTION TO FACTORING
a. Find the greatest common factor, the GCF, of monomials.
b. Factor polynomials when the terms have a common factor, factoring out the greatest common factor.
c. Factor certain expressions with four terms using factoring by grouping.
Objective a
Find the greatest common factor, the GCF, of monomials.

The numbers 20 and 30 have several factors in common, among them 2 and 5. The greatest of these common factors is called the greatest common factor, GCF. One way to find the GCF is by making a list of the factors of each number.
The factors of 20: 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, and 20
The factors of 30: 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 15, and 30
Common numbers: 1, 2, 5, and 10.
The GCF is 10.
Another way to find the GCF is to find the prime factorization of each number. Then draw lines between common factors.
Example A

Example B


Example C

To Find the GCF of Two or more Monomials

Objective b
Factor polynomials when the terms have a common factor, factoring out the greatest common factor.
Factoring When Terms Have a Common Factor

Example D

Example E
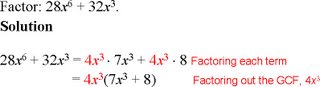
Example F
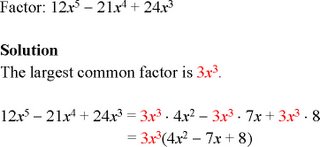
Example G

Example H
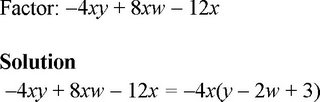

Objective c
Factor certain expressions with four terms using factoring by grouping.
Factoring by Grouping

If a polynomial can be split into groups of terms and the groups share a common factor, then the original polynomial can be factored. This method, known as factoring by grouping, can be tried on any polynomial with four or more terms.
Example J